- Ministary of Education and IBM SkillsBuild 6-Week Free Internship on AI & IBM Cloud Technologies – last date to apply is 3 July 2025
- ICSSR Sponsored Ten-Days Research Methodology Course for Social Science Scholars, Kurukshetra University to Host Intensive Offline Training for M.Phil., Ph.D., and PDF Scholars
- ICSSR Sponsored Ten Days Research Methodology Course for Women Research Scholars in Social Sciences Organised by Department of Studies and Research in Library and Information Science and Karnataka State Open University Library
- A Two Week ICSSR Sponsored Capacity Building Program for the Young Social Sciences Faculty on Entrepreneurship and Startups by INSTITUTE OF PUBLIC ENTERPRISE
- Agricultural Sciences Research Grants worth 50Lac
FTP
File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used to exchange and manipulate files over a TCP/IP-based network, such as the Internet. FTP is built on client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data connections between the client and server applications.
Features of FTP
1. Data representation:
· FTP handles three types of data representations-ASCII (7 bit), EBCDIC (8-bit) and 8- binary data.
· The ASCII file is the default format for transferring text files. Each character is encoded using 7-bit ASCII.
· The sender transforms the file from its own representation into ASCII characters and the receiver transforms the ASCII character to its own representation.
· The image file is the default format for transferring binary files. The file is sent as continuous streams of bits without any interpretation or encoding.
1. File organization and Data structures
· FTP supports both unstructured and structured file.
· An unstructured file contains string of bytes and is enl-marked by EOF (End of file). The data structure that corresponds to such a file is called file structure.
· A structured file contains a list of records and each record is delimited by EDR (End of Record). The data structure of such file is called record structure i.e. file is divided into records.
· Another structured file contains pages, with each page having a page number and a page header. The pages can be stored and accessed randomly or sequentially. The corresponding data structure is called page structure i.e. file is divided into pages.
2. Transmission modes
· FTP can transfer a file by using one of the following three modes:
a) Stream mode
· It is the default mode.
· File is transmitted as continuous stream of bytes to TCP.
· TCP is responsible for chopping data into segments of appropriate size.
b) Block mode
· Data is delivered from FTP to TCP in blocks.
· Each block is preceded by 3 bytes header.
· The first byte is called the block descriptor.
· The second and third byte defines the size of the block in bytes.
c) Compressed mode
· Data is usually compressed if the file to be transmitted is very big.
· The compression method normally used in Run-length encoding.
· In a text file, usually spaces (blanks) are removed. In a binary file, null characters are compressed.
d) Error control
· Since TCP is used for data transfer no additional error recovery mechanism is required.
e) Access control
· File access protection is done using login procedure with login name and password.
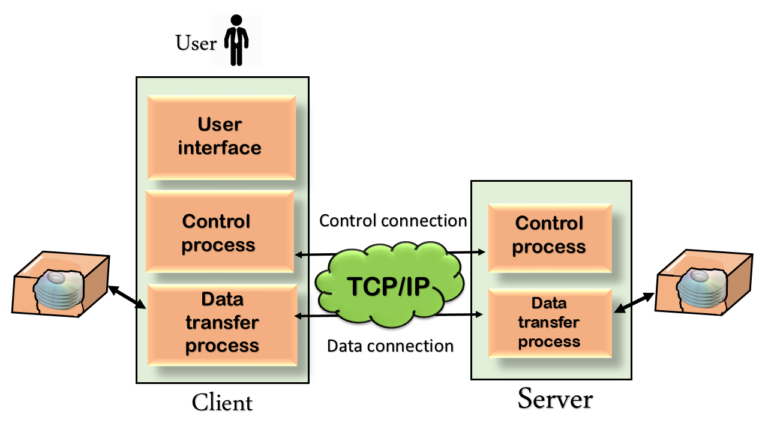
FTP Mechanism
• FTP uses client/server model for communication.
• Two TCP connections are used for file transfer.
• On one connection control signals (commands and responses) are exchanged and the other connection is used for actual data transfer. These two connections are called control connection and data connection respectively.
Control Connection
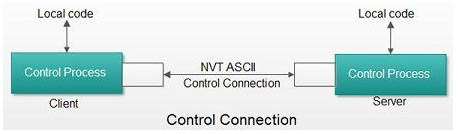
The Control connection has following features:
1. It is used to transfer control signals (commands and responses) between the client and server.
2. This connection is used by the control process of client and server. The control process is called Protocol Interpreter (PI).
3. The TCP connection for control signal uses well-known FTP server port 21.
4. This control connection remains connected during the entire interactive FTP session.
5. The control connection uses very simple rules of communication. We need to transfer only a line of command or a line of response at a time.
Data Connection
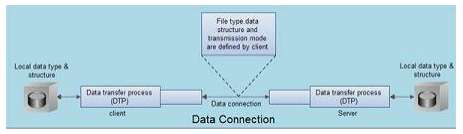
The Data connection has following features:
1. Data connection is used for actual data transfer.
2. This connection is established between the Data Transfer Process (DTP) of client and server
3. The server port used for data connection is Port 20.
4. The data connection is opened and then closed for each file transferred. It opens each time commands that involve transferring files are used, and it closes when the file is transferred.
Thus file transfer in FTP means one of three things:
1. A file is to be copied from the server to the client. This is called retrieving a file. It is done with help of RETR command.
2. A file is to be copied from the client to the server. This is called storing a file. It is done with STOR command.
3. A list of directory or file names is to be sent from the server to the client. This is done with LLST command.
Anonymous FTP
• To Use FTP, a user needs an account (user name) and a password on the Remote server.
• Some sites have a set of files available for public access; to enable anonymous FTP.
• To access these files, a user does not need to have an account or password. Instead, the user can use Anonymous as the user name and guest as the password.
FTP Servers
Similar to the Web servers, the Internet also has the installations of FTP servers. Many organizations use FTP servers to handle the distribution of files. When a user links to download something, the link actually redirects to FTP, instead of HTTP. Some files in the FTP servers may be accessible to the general public, while others are accessible only by the user. To separate the general public from the more private users, FTP servers are divided into two parts:
1. Anonymous Server: Anonymous server is the most common use of FTP, the Internet file transfer protocol. FTP sites that allow anonymous FTP do not require a password for access. You only have to log in as anonymous and enter your e-mail address as password (for their records).
2. Non-anonymous Server: If you use a non-anonymous server, then you will log in as yourself and give your password.
